Proactive Interference AP Psychology Definition: The Key To Memory
In the fascinating realm of cognitive psychology, understanding how our memory functions is crucial, especially when it comes to the concept of proactive interference. This phenomenon occurs when previously learned information interferes with the ability to recall new information, ultimately shaping our memory processes in profound ways. In this blog post, we'll delve into the definition of proactive interference, explore its implications in the context of AP Psychology, and uncover strategies to mitigate its effects on our learning and recall. Whether you're a student preparing for the AP exam or simply curious about the intricacies of memory, this exploration will shed light on why proactive interference is a key player in the way we remember and forget.
Ppt
Proactive interference is a crucial concept in AP Psychology that sheds light on the complexities of memory retention and recall. It occurs when older memories interfere with the retrieval of newer information, making it challenging to learn and remember new material. For example, if you've recently switched phone numbers, your old number may pop into your mind when trying to recall your new one. Understanding proactive interference is essential for students and educators alike, as it highlights the importance of effective study techniques and memory strategies to enhance learning outcomes. By recognizing how past experiences can shape our ability to acquire new knowledge, we can develop more effective approaches to studying and information retention.
 www.slideserve.com
www.slideserve.com Chapter 6 Memory Stage Model Of Memory
In Chapter 6 of our exploration of memory, we delve into the memory stage model, which provides a foundational understanding of how information is processed and retained. This model outlines three crucial stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Encoding is the initial step where sensory information is transformed into a format that can be stored, followed by storage, where this information is maintained over time. Finally, retrieval is the process of accessing and bringing stored memories into consciousness. Understanding this model is essential when examining phenomena like proactive interference, where previously learned information disrupts the recall of new information. By grasping how these stages interact, students can better appreciate the complexities of memory and the factors that influence our ability to learn and remember.
 present5.com
present5.com Interference Psychology
Interference psychology plays a crucial role in understanding how our memories function, particularly in the context of proactive interference. This phenomenon occurs when previously learned information disrupts the recall of new information. For example, if you've recently switched your phone number but keep recalling your old one, it's a classic case of proactive interference at work. In AP Psychology, grasping this concept is essential, as it highlights the complexities of memory retention and retrieval. By recognizing how past experiences can hinder our ability to learn new material, students can develop strategies to mitigate these effects, ultimately enhancing their academic performance and memory retention. Understanding proactive interference not only enriches your knowledge of cognitive processes but also equips you with practical tools for effective studying.
 ar.inspiredpencil.com
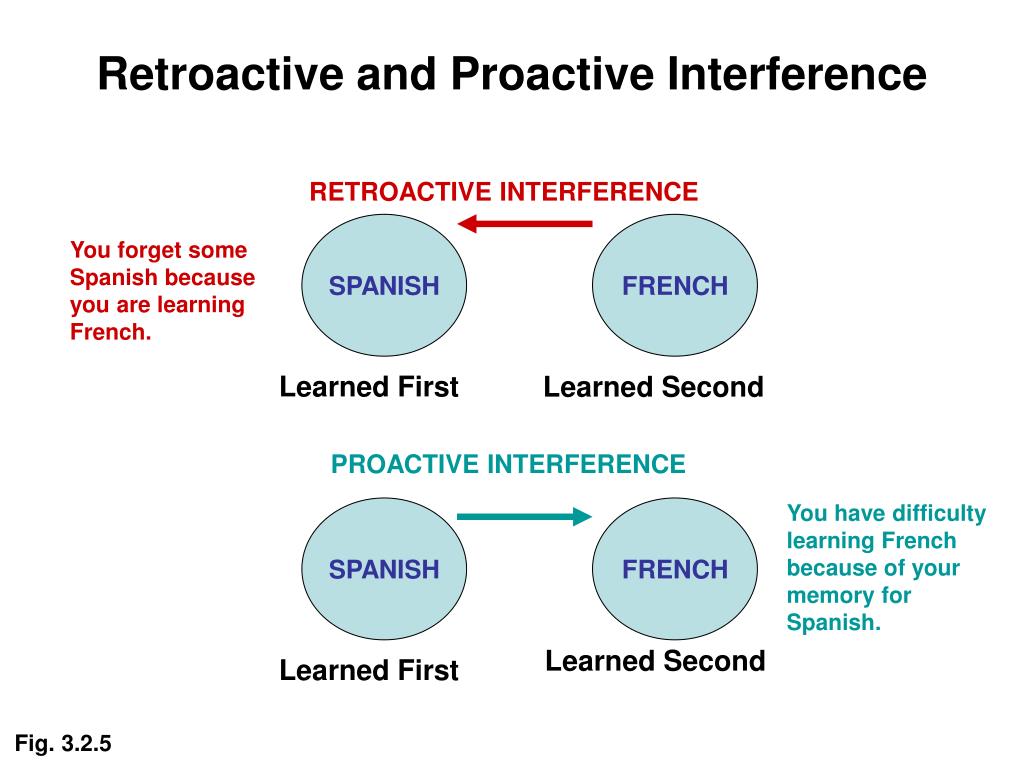
ar.inspiredpencil.com Retroactive And Proactive Interference
In the realm of cognitive psychology, understanding the nuances of memory involves exploring concepts like retroactive and proactive interference. Proactive interference occurs when previously learned information hinders the ability to recall newly acquired information, making it a significant factor in memory retention challenges. Conversely, retroactive interference happens when new information disrupts the retrieval of older memories. Both types of interference illustrate the complex dynamics of how our brains manage and store information, highlighting the importance of recognizing these mechanisms in AP Psychology. By grasping the distinctions between proactive and retroactive interference, students can better appreciate the intricacies of memory and its implications for learning and recall.
 sites.psu.edu
sites.psu.edu 8. Interference (memory)
You Might Also Like: Allen Meredith Correctional Facility
Proactive interference is a crucial concept in understanding memory, particularly in the context of AP Psychology. It occurs when older memories disrupt the retrieval of newer information. For instance, if you've recently moved to a new address but keep recalling your old one instead, that's proactive interference at play. This phenomenon highlights the complexity of our memory systems, illustrating how previously learned information can overshadow new experiences. Recognizing proactive interference is essential for students, as it not only helps clarify why certain memories fade or confuse but also provides insights into effective study techniques. By understanding how past knowledge influences current learning, students can develop strategies to minimize interference and enhance their retention of new material.
 www.tes.com
www.tes.com